燕麦对碱胁迫的阳离子响应机制
 , 刘景辉
, 刘景辉 , 刘伟
, 刘伟Cation-Responsive Mechanisms of Oats to Alkali Stress
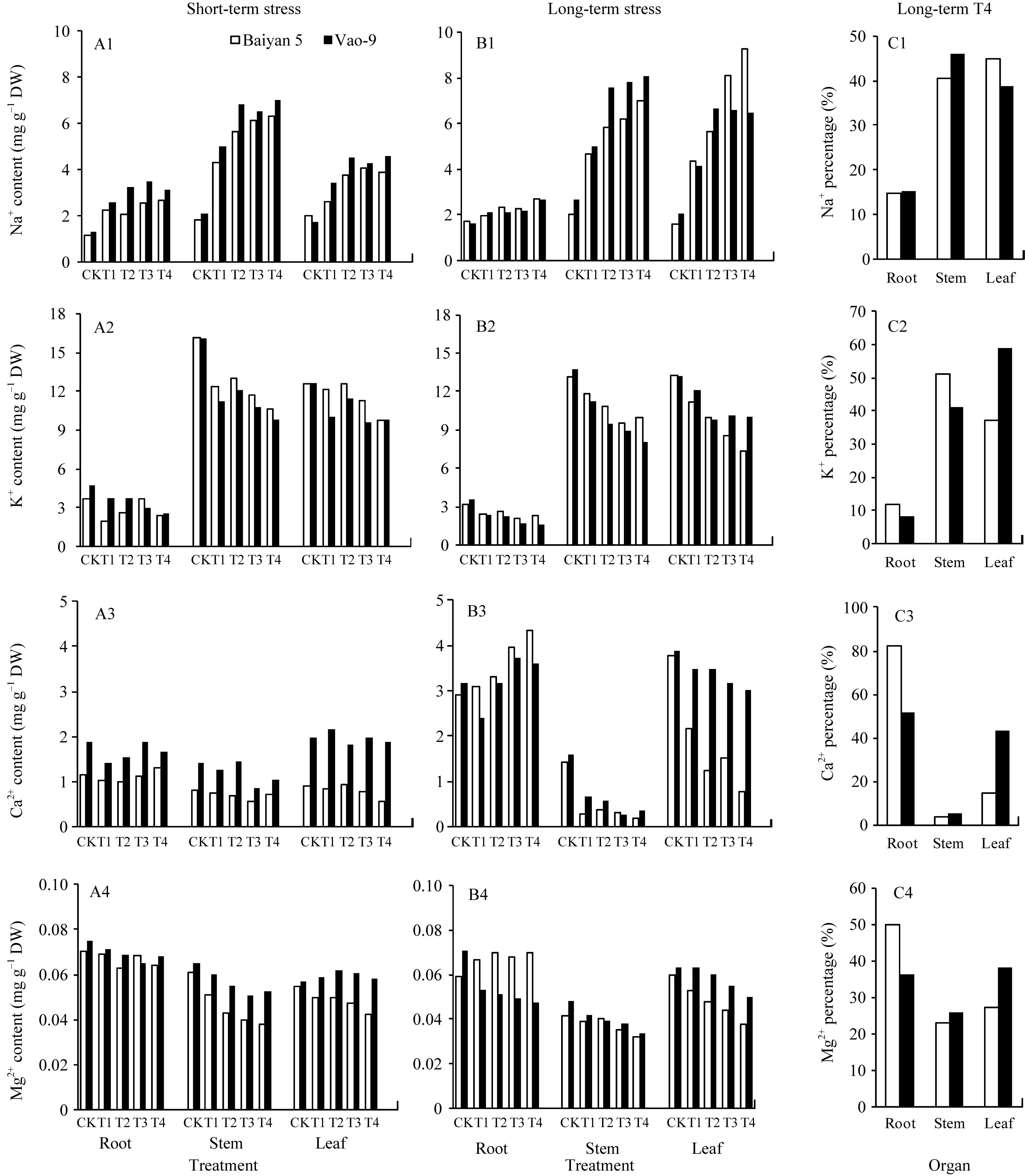
Fig. 1 Contents and distribution ratios of four cations in root, stem, and leaf of oat under different concentrations of alkali stress Alkali concentrations in different treatments were 0 CK, 25 T1, 50 T2, 75 T3, and 100 mmol L -1 T4 under both short-term 14 d and long-term 28 d stress.