磷肥对甜玉米籽粒植酸和锌有效性的影响
Effects of phosphorus fertilizer on kernel phytic acid and zinc bioavailability in sweet corn
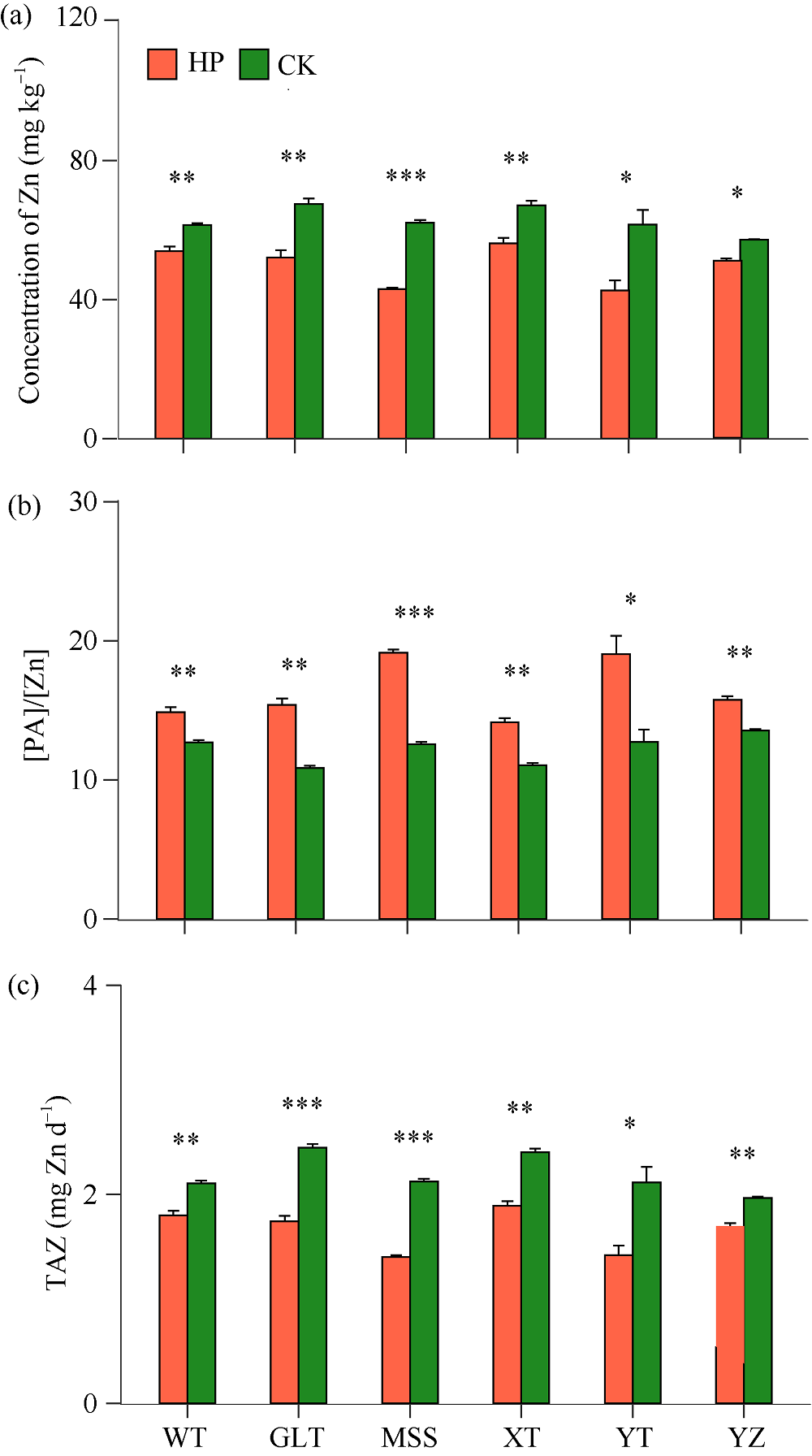
CK: 无磷肥处理; HP: 高磷肥处理。*、**和***分别代表同一品种内两种磷水平下的差异显著性达0.05、0.01和0.001水平。Zn: 锌; [PA]/[Zn]: 植酸与锌的摩尔比; TAZ: Zn有效性; WT: 万甜2015号; GLT: 广良甜31号; MSS: 闽双色4号; XT: 先甜5号; YT: 粤甜28号; YZ: 永珍7号。
CK: no phosphorus treatment; HP: high phosphorus treatment. WT, GLT, MSS, XT, YT, and YZ represent Wantian 2015, Guangliangtian 31, Minshuangse 4, Xiantian 5, Yuetian 28, and Yongzhen 7, respectively. [PA]/[Zn]: the molar ratio of phytic acid to zinc, TAZ: Zn bioavailability. The symbols *,** and *** represent the significant differences at P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.001 in the same variety under two phosphorus treatments, respectively.