基于氮肥运筹下水稻产量与品质协同的农艺生理指标解析
Analysis of agronomic and physiological indicators of rice yield and grain quality under nitrogen fertilization management
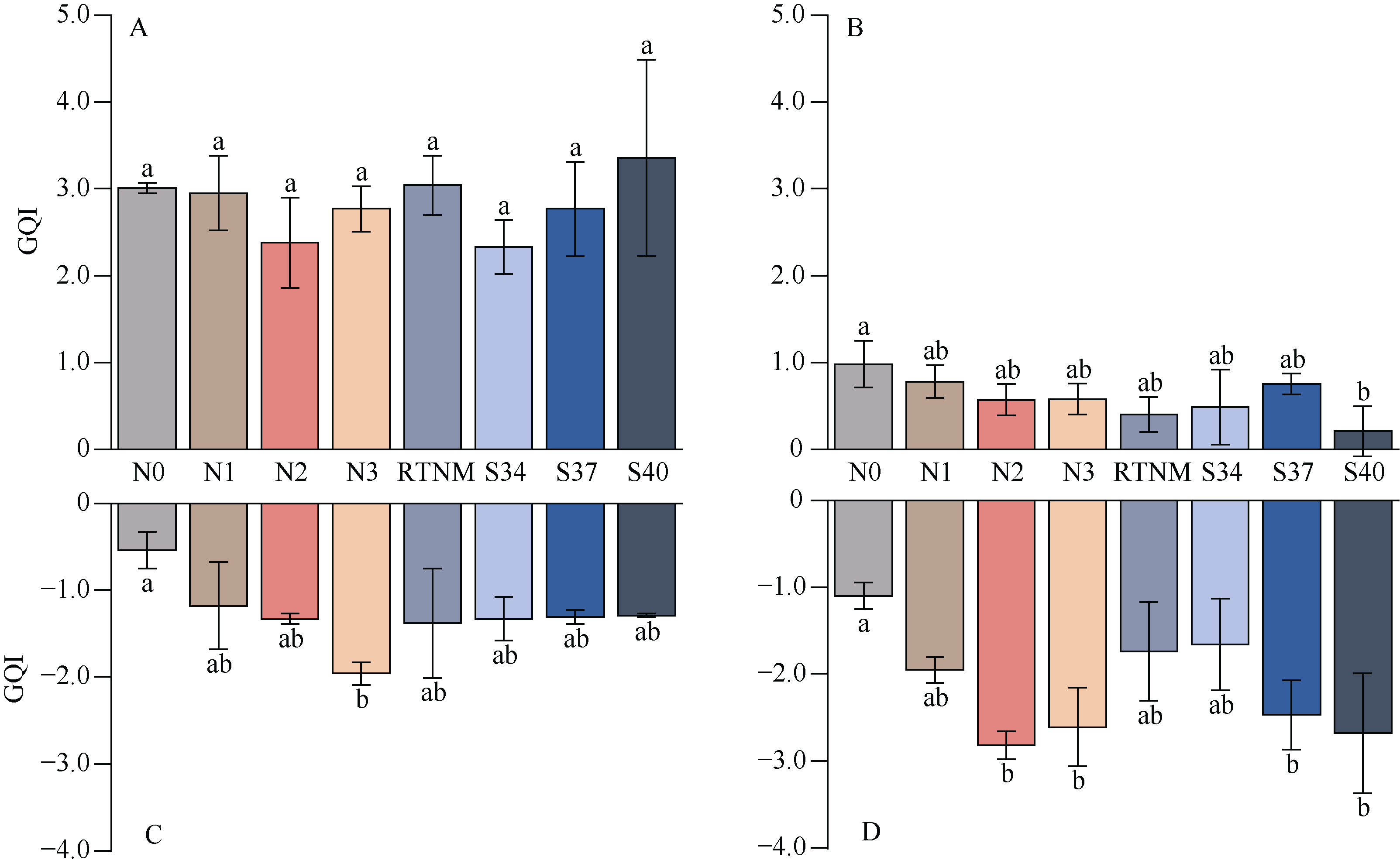
A、B分别代表2021-2022年氮肥运筹对水稻XS134中GQI的影响; C、D分别代表2021-2022年氮肥运筹对水稻HHZ中GQI的影响。GQI: 稻米综合指标。图中误差棒表示标准误, 不同小写字母表示不同氮肥处理间差异显著(P < 0.05, LSD)。处理及缩写同
A and B represent the effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on the GQI of rice variety XS134 in the 2021-2022 seasons; C and D represent the effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on the GQI of rice variety HHZ in the 2021-2022 seasons. GQI: grain quality index. Error bars in the figure represent standard error, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different nitrogen fertilizer treatments (P < 0.05, LSD). Treatments and abbreviations are the same as those given in