Welcome to Acta Agronomica Sinica,
|
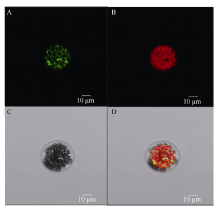 Subcellular localization of BnA7HSP70 and GFP fusion protein in Arabidopsis protoplasts.
Subcellular localization of BnA7HSP70 and GFP fusion protein in Arabidopsis protoplasts.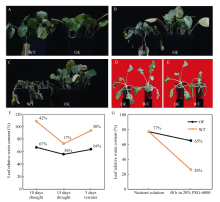 BnA7HSP70 overexpressed (OE) plants confer tolerance under a restricted water regime and 20% PEG treatment
BnA7HSP70 overexpressed (OE) plants confer tolerance under a restricted water regime and 20% PEG treatment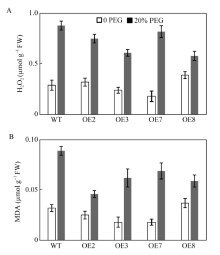 Changes of H2O2 content and MDA levels in wild plant and transgenic plant line under 20% PEG treatment.
Changes of H2O2 content and MDA levels in wild plant and transgenic plant line under 20% PEG treatment.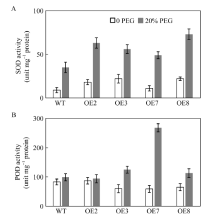 Antioxidant enzyme activities in wild plant and transgenic plants after treatment with 20% PEG
Antioxidant enzyme activities in wild plant and transgenic plants after treatment with 20% PEG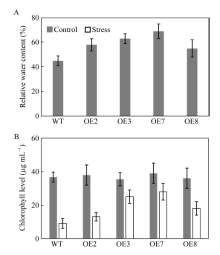 Overexpression of BnA7HSP70 makes Brassica napus hold more water in soil pot without irrigation for 10 days
Overexpression of BnA7HSP70 makes Brassica napus hold more water in soil pot without irrigation for 10 days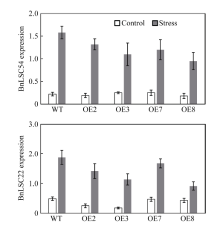 BnA7HSP70 overexpression delays drought-induced leaf senescence in OE lines confronted with stress
BnA7HSP70 overexpression delays drought-induced leaf senescence in OE lines confronted with stress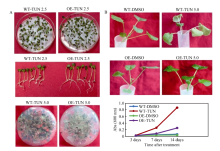 BnA7HSP70 overexpression increases resistance against tunicamycin (TUN)-induced cell death
BnA7HSP70 overexpression increases resistance against tunicamycin (TUN)-induced cell death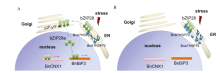 Model for BnA7HSP70 expression on the mobilization of bZIP28 and upregulation of UPR genes
Model for BnA7HSP70 expression on the mobilization of bZIP28 and upregulation of UPR genes Performance of FHB resistance in the backcrossing progenies with or without Fhb1 gene from different donors, recurrent parent and controls using the floret-inoculation method
Performance of FHB resistance in the backcrossing progenies with or without Fhb1 gene from different donors, recurrent parent and controls using the floret-inoculation method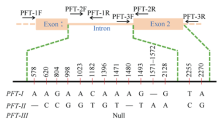 Structure, primer binding sites and three alleles of PFT gene
Structure, primer binding sites and three alleles of PFT gene Amplification profiles of marker PFT-CAPS in partial Chinese cultivars
Amplification profiles of marker PFT-CAPS in partial Chinese cultivars Amplification profiles of marker His-InDel in partial Chinese cultivars
Amplification profiles of marker His-InDel in partial Chinese cultivars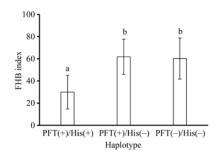 Average FHB indexes of cultivars or lines with different PFT/His haplotypes
Average FHB indexes of cultivars or lines with different PFT/His haplotypes
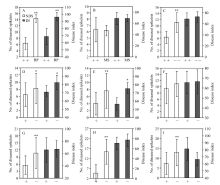 Comparison of number of diseased spikelets and disease index between backcrossing progenies with Fhb1 gene from different donors and recurrent parent, moderately susceptible control and the backcrossing progenies without Fhb1 gene
Comparison of number of diseased spikelets and disease index between backcrossing progenies with Fhb1 gene from different donors and recurrent parent, moderately susceptible control and the backcrossing progenies without Fhb1 gene| First page | Prev page | Next page | Last page | Page1 of 818, 16351records |